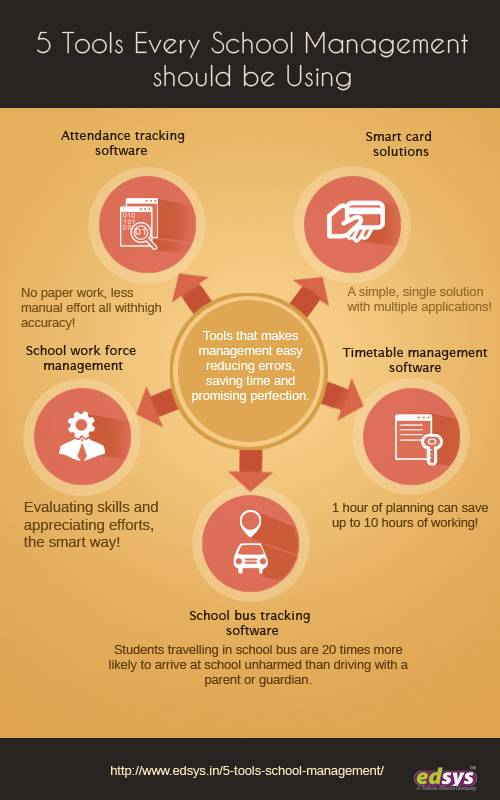
Attendance is an important everyday school activity. A decade ago, attendance was taken at schools by calling out everyone’s name. Now, technology has made the process easier and faster. You might be familiar with biometric systems.
RFID technology is currently the most popular and feasible technology used for School Attendance Systems, student tracking systems and parent portals.
What is an RFID Attendance System?
An RFID Attendance System makes use of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags to log the attendance of individual students to database. A database would have unique profiles for individual students with details such as their address, date of birth, class, etc which can be viewed through school apps or parent portals.
Types of RFID Attendance Systems
There are two main types of RFID Attendance systems- Passive and Active according to the types of tags used.
- Passive RFID
In this type, RFID readers would send radio waves to tags. The microchip in the tags power on using this signal and reflect back the signal to the reader. Thus the time of entry/exit gets registered in the database. It is due to this very reason that these are known as “Passive RFID”
These can operate in three different radio frequencies:
125 – 134 kHz – LF (Low Frequency)
13.56 MHz – HF (High Frequency)
856 MHz to 960 MHz – UHF (Ultra High Frequency)
The range of Passive RFIDs is limited as it simply reflects signals back to the reader rather than emitting signals on its own. Therefore, the range of these tags usually comes under 10 meters. However, this gives it several advantages.
Advantages
- It doesn’t require a power source
- Smaller in size
- Easy to manufacture
- Far more cheaper than Active RFID
- Minimal health hazards
Being extremely affordable, it is no surprise that these are the most widely used RFID tags. Because of their simple nature, Passive RFIDs have numerous applications. Attendance at schools and offices commonly use these.
Battery Operated Passive Tags: These are similar to normal passive RFID tags. The only difference is the addition of a battery to power on the microchip. This helps to use the entire signal received from readers to be reflected back instead of using it to power on the microchip. Thus, it effectively improves the range.
- Active RFID
Unlike Passive RFID systems, these use RFID tags that have their own power source and a transmitter. Active RFIDs have superior range and data capacity. Some of these tags are known to have range over 100 meters. But these increased abilities come with an increased demand for power.
These are usually powered by powerful batteries which can last for a few years. Never the less, they have to be replaced once the batteries expire. There are two types of Active tags – Transponders and Beacons
a) Transponders wake up by receiving radio signals from their readers. Once awake, they communicate with the readers as required. As they do not use their battery power to wake up, transponders have better longevity compared to Beacons.
b) Beacons are used for real-time location monitoring systems. They are powered by their own batteries and emit signals at pre-determined intervals.
Advantages
- Long range
- Ideal for real-time location systems
- Larger memory
However, there are numerous aspects that make Active RFID tags less feasible for large scale usage. The improved technology in Active RFID tags make them costlier and the associated radiation could be hazardous to health. Also, they are usually bulky when compared to passive tags. Hence schools and offices usually prefer passive tags for attendance while active tags are used in throughout supply chains and shipping yards.
Wi-Fi: The Future of Attendance Systems
Technology is developing rapidly, and Wi-Fi seems to be a faster, more user-friendly option as far as attendance systems is concerned. With BYOD in schools and workplaces becoming a popular trend, concerned authorities would not have to invest in hardware. However, the technology is still in evolving stage.