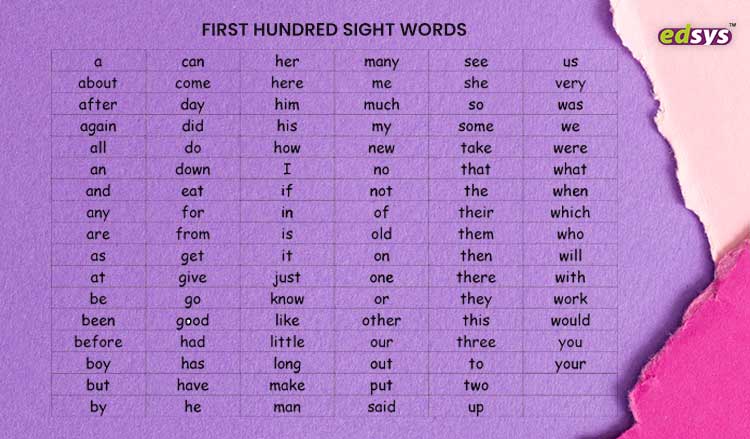
If you have noticed that your child has poor handwriting, then the chances are that they are facing Dysgraphia. In the U.S. alone, over 17 percent of the population faces this issue, and many among them are not even aware of it.
However, through this post, you will come to know about this condition in detail. It will also give you the right way of helping your child overcome this condition if he or she has it.
Let’s get started.
What is Dysgraphia?

Dysgraphia is a condition that affects an individual’s writing ability.
Dysgraphia can exist in the form of problems involving poor handwriting, spelling, and lacking the ability to write expressive content. Dysgraphia can exist as a linguistic or/and non-linguistic disability.
Do not confuse Dysgraphia with poor handwriting, as it is a severe neurological condition. It is usually seen in children during their initial days of learning the ability to write. There is a lack of solid proof that explains why this happens, but treating at an early stage can help reduce or prevent this issue.
When you hold a pen or pencil to write, it feels quite natural to you. But, the process is complicated in reality. It needs intricate processing and motor skills to shape the words on paper. An average person can do it with ease due to a healthy condition. But, the same is not the case for a person with Dysgraphia.
Writing needs an individual to operate the finger and hand muscles to express ideas in the form of letters on paper.
Furthermore, Dysgraphia, which is due to a linguistic disability, may be identified to exist in a person based on his/her difficulty to transform language sounds to written symbols.
It can also be characterized by his/her lack of understanding about which spelling is usable for individual sounds.
Also Read: 10 Reasons Why Students Fail Mathematics
Someone with Dysgraphia may mistake the correct alignment of letters, and they might end up writing letters in reverse.
They may lack the ability to remember the accurate positioning of symbols or to use upper- or lowercase letters.
Additionally, an individual with Dysgraphia may find it troubling to write sentences with proper punctuation and grammar. Such a person may show issues like:
- Improper placement of words
- Incorrect use of verbs
- Omitting words
- Wrong utilization of ending words
- Error in the usage of pronouns
Despite the lack of ability to write sentences correctly, people with this condition may communicate verbally with ease and fluency.
As for people with non-linguistic driven Dysgraphia, there is a lack of coordination of motor skills while writing.
The general term of reference for this condition is apraxia, which in itself comprises of several types of motor skill disorders.
So, there is an impairment in the proper execution of motor skills to perform purposeful movements.
What Are The Different Types of Dysgraphia?
Five distinct types of Dysgraphia exist medically. Some kids may also show more than one kind of Dysgraphia in them. It should be noted that the actual symptoms may vary from the ones listed under each type.

1) Dyslexic Dysgraphia
In dyslexic Dysgraphia, an individual may be able to copy signs and symbols correctly but may lack the ability to write correct spellings. Furthermore, he/she may write illegible sentences when written spontaneously. A person with Dyslexia Dysgraphia may or may not have Dyslexia. The finger tapping test (FTT), which is used for testing the motor speed skills, are regular in such a person.
2) Motor Dysgraphia
This medical condition is because of a lack of functioning motor skills, poor muscle tone, and reduced ability. The affected person may also show clumsiness.
His/her writing abilities, including coping skills, are also illegible or deficient. Such an individual may be able to form short writing samples, but that too needs a lot of effort and time to accomplish at an acceptable level – which is not appropriate for practicality. There is also slant in the writing style as the person is unable to hold a pencil or pen correctly. Spellings might still be fine in this case.The FTT speeds for such an individual are below average.
3) Spatial Dysgraphia
This disability is present in those who cannot understand space. The work written spontaneously is illegible in such a person. Even the copied work is illegible.
However, students suffering from spatial Dysgraphia may write normal spelling and show average FTT speeds.
Such students may also find it hard to write with proper spacing between words and keep the letters within lines.
4) Phonological Dysgraphia
This type of Dysgraphia causes impairment of phonetically irregular and unfamiliar words in the affected individual. Such people cannot also recall phonemes (the unit of sound to differentiate one linguistic word from another) or use the appropriate to create a word.
5) Lexical Dysgraphia
Lexical Dysgraphia is present in an individual who is unable to distinguish patterns generated from sounds to create letters for words.
As a result, they often end up creating irregular or misspelled words. Such a case is generally seen in less-phonetic languages like French and English. Children rarely face this type of Dysgraphia.
Causes of Dysgraphia
Here is a list of reasons for Dysgraphia. These issues may or may not be found in dyslexia as well.
1) Brain Damage
Brain damage usually takes place when oxygen supply is reduced to the organ. This can happen due to:
- Head stroke or injury
- an effect of high temperature
- a near-drowning experience
An individual affected by brain damage can have poor handwriting. Developing legible handwriting for such a person is delayed, but achievable. For facilitating that, such a person may require care and affection to improve.
2) Deformity or physical illness
This can occur in a child due to an accident, an illness, or a birth defect.
If he/she has paralysis due to a damaged nerve(s), then his/her handwriting may suffer. The issue, in some cases, can be improvised by patients to write legibly.
3) The intentionally bad writing style
This one may not have a direct relation to Dysgraphia or dyslexia, but several individuals who do this might have a high probability of being dyslexic.
People who write bad grammar, punctuation, or spellings may end up with poor handwriting intentionally so that they can hide their lack of skills.
Such limitations can be a cause of Dysgraphia. This issue can be dealt with if the student is monitored for his use of grammar, punctuation, and spellings while instructing him to write legibly.
But, poor writing is not always the case. Some may show signs of confusion neurologically. The other steps might have to be taken.
4) Lack of Instructions
Some students do not get the necessary instructions to practice legible writing from the beginning. The development of Dysgraphia or dyslexia in such children is common.
It might be possible that they did receive guidance, but their ability to grasp those methods might have been limited. Due to disorientation in the child, he/she might not have been able to understand the instructions for writing correctly.
In such a case, a parent or teacher, involved with the kid, might not have been able to realize that the child was confused about the simple instructions given to other kids with normal motor functioning.
Once the confusion of the child is amended, his/her ability to write legibly is accomplished. Then the child can also be taught the right way of penmanship to create the letters and symbols properly.
5) Disorientation
This is a condition where a person cannot focus when there is a need to process motor skills to accomplish a task.

When disorientation is related to Dysgraphia, then a person with this issue may not have proper coordination to write words, letters, or symbols.
A person, who is in an orientated state, witnesses a catalyst that causes him/her to become disoriented, maybe for a very short period. But, this split-second confusion causes his/her writing to become illegible.
The disorientation in a child might be possible when he/she gets stimulated due to sudden action. This action is usually not related to an external object, but due to emotion from within.
It might be confusing that causes someone to disorient from a writing task, just like in dyslexia. Most people, who suffer from dyslexia, face disorientation when they see befuddling letters and symbols.
Most students are able to deal with this when the confusing word is accompanied by a picture or an illustration.
But, how words that do not accompany images, confused them.
This happens as dyslexics perceive words with their meanings and visual representations, not with the word groups or sounds. Overall, a disoriented student is likely to develop Dysgraphia.
6) Thinking Several Images in the Mind
Many individuals with Dysgraphia can picture the exact image of a word to copy it correctly on paper. But, when the same word is being taught to them to be written in multiple styles, they end up with too much pressure on the mind.
For instance, a child is trying to copy his/her name from the blackboard which his/her teacher wrote. The kid has a clear picture of how the word is to be spelled.
But, suddenly the teacher writes the same name again in a slightly different way, leading to confusion in the mind of the child.
Plus, the teacher gives several instructions to the child to spell the name in a specific order. This can result in the kid developing unusual motor skills, like holding the pencil too tight, becoming anxious, and whatnot. As a result, he might end up with Dysgraphia.
Symptoms of Dysgraphia
People can show the following signs that may increase their chances of developing Dysgraphia:
1) Improper Formation of Letters
A dysgraphic child may find it hard to understand the combination of curves and lines. It might be struggling for him or her to produce letters and copying pen strokes.
It might also be difficult for the child to conclude the size and spacing of the letters.
This is noticeable from the starting of the learning stage of the child, as he or she struggles to write in a normal way like other children of the same age.
There may also be a disproportionate pattern in the letters. Writing lowercase letters may be a daunting task for them, as they are usually smaller in size and have more curved lines than uppercase ones.
This makes it harder for them to wield a pencil or pen. This symptom may also show signs of reverse letters, unnecessary capitalizations, lack of ability to write in cursive, etc.
Overall the letters produced are mostly illegible.
2) Frustration and Pain While Writing
Kids with Dysgraphia also grumble about a hurting hand while writing. This is due to a lack of development of motor skills to write healthily.
They might have an inappropriate elbow and wrist position that makes it harder for them to withstand the grip for prolonged intervals.
At times such children may have it difficult to keep the paper aligned under their hands, as they cannot apply the pressure calculatedly to keep it steady.
All such issues distract them and prevent them from writing letters on paper thoughtfully. There is also a complaint of strained posture and unnatural movements during writing.
3) Spacing Issues
Symptoms related to Dysgraphia can also include spacing problems between sentences, words, or/and letters. It can be challenging for such individuals to produce text from right to left.
They also find it hard to keep letters in a straight line, especially when writing equations in mathematics. You will often witness that a person with Dysgraphia will have trouble writing in tiny boxes like in a maths notebook.
4) Poor Spelling
With troubled writing abilities, children with Dysgraphia are often poor at spellings. They will make mistakes quite frequently while writing words. Moreover, the English language has so many intricate rules that are confusing for such kids to follow.
5) Hesitation To Complete Work
With so many writing issues, such children will show signs of avoiding schoolwork. Their inabilities to write error-free and legibly makes them hesitant to complete work at school or home. Their abilities to work efficiently even makes them skip school days, leading to a decline in their performance.
6) Lack of Confidence
Children who may have Dysgraphia also feel negative about their self-image. Such individuals frequently get embarrassed when they have to write something on paper. This can further lead them to perceive themselves poorly.
Diagnosing Dysgraphia
To learn whether a child is suffering from Dysgraphia or not, a pediatrician will diagnose him or her. However, the doctor will also make sure to see if some other illness or disorder might not be the case.
Once other illnesses are ruled out, an accredited psychologist who knows how to deal with learning conditions will help you diagnose your child for Dysgraphia. Even a psychologist present at your child’s school can help with that if he or she is qualified.
Such a specialist will start with certain writing and academic assessments that will calibrate the abilities of the child. Such tests are a way to see the coordination between the child’s thoughts and motor skills.
Some common ways of diagnosing children for Dysgraphia that doctors use are:
- Instructing the child to rotate his or her wrist in a particular way.
- Making the kid tap his or her fingers.
- Asking the child to write words or sentences or to copy letters.
While involving a child in such activities, the psychologist will try to examine his or her writing process, posture, pencil grip, body and hand position, and the completed work.
Treatment For Dysgraphia
You might not be able to find a promised cure for Dysgraphia. However, the treatment differs individually.

Each child may need to be treated in a varying way to help him or her get over the condition. Some doctors also prescribe medications that are often used for ADHD as well.
How Can I Help My Child?
Parents can help their children with Dysgraphia are some of the following ways:
- Make your child learn the various letters through touching rather than seeing. For instance, you can draw the symbols on their hands so they can understand how each symbol can be written.
- Have your kid practice creating letters with the help of graph paper, ruler, etc. That will help them align words better.
- Teach the child to write big so that it is easier to understand how the letters need to be created. With time, you can make them practice writing smaller letters gradually.
- Children can also use clay to create letters and symbols to practice while enjoying. This also decreases the pressure they have built due to Dysgraphia.
- Avoid criticizing them when they are writing, even if the work is sloppy. Always praise them for the efforts and encourage them to improve further.
- You can make your child use various pencil grips that will help to write comfortably.
- Use stress-relieving balls that children can squeeze to release strain on their hands. That will improve their writing skills.
- Teach other exercises that will help them reduce their stress before writing. Some routines include rubbing together, rotating wrists, etc.
- Besides writing, let them learn typing on a computer as well. Make them familiarize the letters as early as possible.
- Have them work out to improve their muscles and overall physical stability. A strong body is likely to write efficiently.
- Let them speak the words and symbols as they write on the paper. Also, remember to make them write while holding the paper with the other hand for better coordination of motor skills.
Conclusion
Dysgraphia is more of a challenge that can be overcome with the right guidance. Sometimes all it takes is a push to make a child get over the condition. On the other hand, children can also face this problem lifelong.
Also Read: General Knowledge for Kids with Answers (105 Q & A)
Children with Dysgraphia can feel better through efforts made by their parents or with the help of capable doctors. If your child has been facing issues like Dysgraphia, then make sure to create a training regimen for them to get better at their writing skills.