Driverless cars have been a sci-fi lover’s dream for a long time. There is something inherently cool with the idea of travelling in a driverless car. When Google finally made self driving cars a reality, their design was completely different from the kind we see in Hollywood sci-fi movies. Maybe due to this, these cars did not evoke a positive response from the public. However, the Internet giant used the cars for collecting data for its street view maps.
Slowly, more and more people became impressed with Google’s effort. As of April 2014, the team of Google’s self driving cars has covered close to 700,000 autonomous miles (1.1 million km) in open road. Most of this has been in California where Google has created a virtual road map for its cars. Despite that it is an impressive feat.
The Secret of Google’s Self Driving Cars
So, what is the technology that made Google’s autonomous cars possible? The answer is around us. Most of the technology is already in cars that are on the road such as automatic breaking and parallel parking seen in some of the latest model cars. Some cars even have advanced cruise control that helps to keep the car inside the lane mark. The technology behind Google’s self driving cars when viewed individually is more evolutionary than revolutionary.
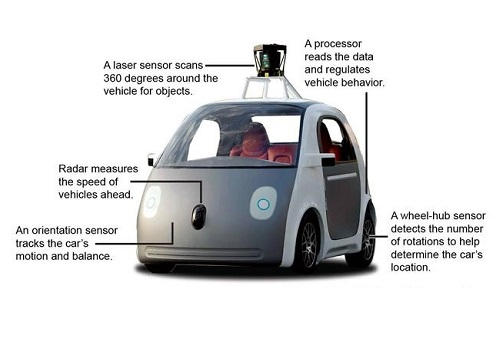
An assortment of sensors is used to generate a map of the surrounding area and compare it with the map in Google’s database. By doing this, the car is able to understand the original path and identify the new objects (people, other vehicles and more) for easier navigation. The major or most interesting among the eight different sensors used in these self driving cars is named Lidar. It is a rotating sensor placed at the roof top which helps build 3D maps at a distance of 200m continuously by the use of 32/64 lasers. The car also has a set up that monitors other motorists and pedestrians using a standard camera.
Role of GPS Technology
You might be familiar with GPS technology which helps in geo-location in your smartphone. A more sophisticated version of the same used in Google’s autonomous cars. GPS technology is quite popular as it is used in several applications such as vehicle tracking systems and school bus tracking systems apart from smart devices. In Google’s cars, a GPS aerial is mounted at the rear for location information. But these cars also feature gyroscopes, altimeters and a tachometer in them to avoid even a minute miscalculation of cars’ positions.
Mishaps
Despite the technology involved, there has been couple of accidents that involved the search giant’s driverless cars. The first one occurred back in 2011 near the company’s headquarters in California. Another time, a self driving car from the Google stable was rear ended at a traffic light. But Google clarified that both the cars were being driven manually when the incidents occurred.
Commercialization and recent developments
Google doesn’t have plans to commercialize driverless cars immediately. But there have been some recent developments such as Nevada becoming the first US district to make autonomous cars legal and UK allowing driverless cars in its roads from 2015. These might prompt Google to bring the autonomous cars on the roads faster than expected.
Recently it was confirmed that Google’s self driving cars are designed to exceed the speed limit by almost 10 Kms/hr in order to keep up with other cars if they exceed the speed limit. Thus it’s pretty clear that these cars are very close to being commercialized. Also, Google recently announced plans for 100 self-driving car prototypes
Hurdles faced by Driverless cars
But there are some hurdles that Google and other promoters of the technology need to tackle before full commercialization. One is the legal implications and the other is the general public’s attitude towards cars without drivers.
It might even take a generation before people become comfortable with the idea of travelling in cars that have no drivers. While the time frame is uncertain, most developed nations are sure about one thing – that autonomous vehicles are the future.
Facts about Google’s Self Driving Car Prototypes
- They run 100% on electricity. Talk about a greener future!
- When fully charged, these cars will be able to run for 100 miles
- You can use your smart phone to summon these cars
- It is not confirmed at the moment, but these cars may not have pedals and steering wheels
- Google’s Self Driving prototypes use a complex mechanism which uses radars, lasers and sensors other than GPS systems for navigation
- These cars won’t be manufactured commercially. Google would probably partner with a car manufacturer to bring this technology to the market
- car crashes are due to driver errors According to experts, driverless cars can reduce the number of accidents that happen on road. Reason? Most reports point out that more than 85% of. So, autonomous cars while unable to completely eliminate crashes; will reduce the rate of accidents drastically.
- If commercialized, driverless cars will lead to a massive rewriting of traffic rules